SOLIDWORKS C# API - Test ApplyUnitConversion Method
Objective
I want to:
- Test
ApplyUnitConversionMethod. - I will not explain each line, since they are already explained in previous articles.
- We will continue from previous article 🚀 Test Create Line Method.
Demo Video
Watch the video below to learn how to Test ApplyUnitConversion Method.
Please note that there are no explanation in the video.
Explanation of each step and why we write code this way is given in this post.
Modify [MainWindowViewModel]
First, we need to make ApplyUnitConversion method we going to use in our test class make as public.
public (double, double, double) ApplyUnitConversion(IPointViewModel inputPoint, double lengthConversionFactor)
{
double X, Y, Z;
X = inputPoint.XPoint * lengthConversionFactor;
Y = inputPoint.YPoint * lengthConversionFactor;
Z = inputPoint.ZPoint * lengthConversionFactor;
return (X, Y, Z);
}
Above changes we need to do in our MainWindowViewModel class.
Add Test Cases
To test ApplyUnitConversion method we need to add below 👇🏻 test cases.
- Test 1 - ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates
- Test 2 - ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates
- Test 3 - ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates
- Test 4 - ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates
- Test 5 - ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates
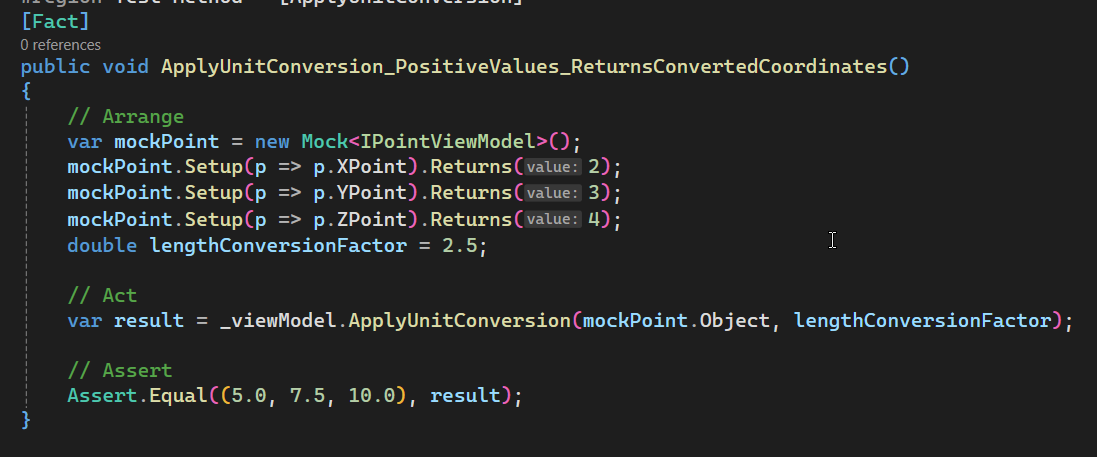
Add [Test 1]
In this section, we set up ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates.
Please see below 👇🏻 code sample for set up.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates()
{
// Arrange
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
double lengthConversionFactor = 2.5;
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
// Assert
Assert.Equal((5.0, 7.5, 10.0), result);
}
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
Explanation of above ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates is give below.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates()
{
}
[Fact]:- This is a test attribute.
- This attribute shows that this method is a test case that the
xUnittest runner recognizes.
public:- This means that the
ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinatesmethod can be accessed from anywhere. - This is important, because
xUnittest runner is external agent. xUnittest runner need to have accessed to thisApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinatesmethod.- Because of this requirment we need to give
publicaccessor.
- This means that the
void:- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinatesmethod. - Generally we don’t return anything from test method.
- Because of this we return
voidmeans we are not returning anything.
- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_PositiveValues_ReturnsConvertedCoordinates- This is the name of method.
- This name is created in 3 different parts and combined with underscore “_“.
- Different parts are explained below 👇🏻:
- Part 1: Name of method we are testing.
- Part 2: Return value we are expecting.
- Part 3: Condition for which we are testing the method.
First we arrange our test method and setup variables and methods before testing.
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
-
var: This is a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable. -
mockPoint: This is name of object we want to create. -
new: This is a keyword that creates a new instance of a class. -
Mock<IPointViewModel>():Mockis the class that creates a “mock” object, which is a fake version of a real object.- In our case, it’s a mock version of the
IPointViewModelobject.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPointis the variable we created previously.Setupis a method that sets up the mock object to behave in a certain way.p => p.XPointis a lambda expression that says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty of this mock object, do something”.Returns(2)says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty, return the value2”. This means that if someone tries to get theX-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be 2.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
YPointproperty to return the value3. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Y-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be3.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
ZPointproperty to return the value4. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Z-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be4.
double lengthConversionFactor = 2.5;
doubleis a data type that means “a decimal number”.lengthConversionFactoris the name of the variable.2.5is the value assigned to the variable.- This line creates a new variable called
lengthConversionFactorand sets its value to2.5.
Now we finished with our arrangement part, we will now continue with Act part of our test method.
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
varis a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable.resultis the name of the variable._viewModelis an object that represents theMainWindowViewModelview model.ApplyUnitConversionis a method of theMainWindowViewModelview model that applies a unit conversion to a point.mockPoint.Objectis the mock point object that we created earlier, which has X, Y, and Z coordinates set to 2, 3, and 4 respectively.lengthConversionFactoris the conversion factor that we defined earlier, which is 2.5.- This line of code is calling the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod on theMainWindowViewModelview model, passing in the mock point and the conversion factor, and storing the result in theresultvariable.
With this we finished with Act part of our test method. Now we will continue with Assert part.
// Assert
Assert.Equal((5.0, 7.5, 10.0), result);
Assertis a keyword in xUnit testing framework and is used to verify that a certain condition is true.Equalis a method of theAssertclass that checks if two values are equal.(5.0, 7.5, 10.0)is a tuple that represents the expected result. In this case, it’s a 3D point with X, Y, and Z coordinates.resultis the variable that holds the actual result of theApplyUnitConversionmethod, which we explained earlier.- Above line of code is checking if the actual result of the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod is equal to the expected result, which is the point(5.0, 7.5, 10.0).
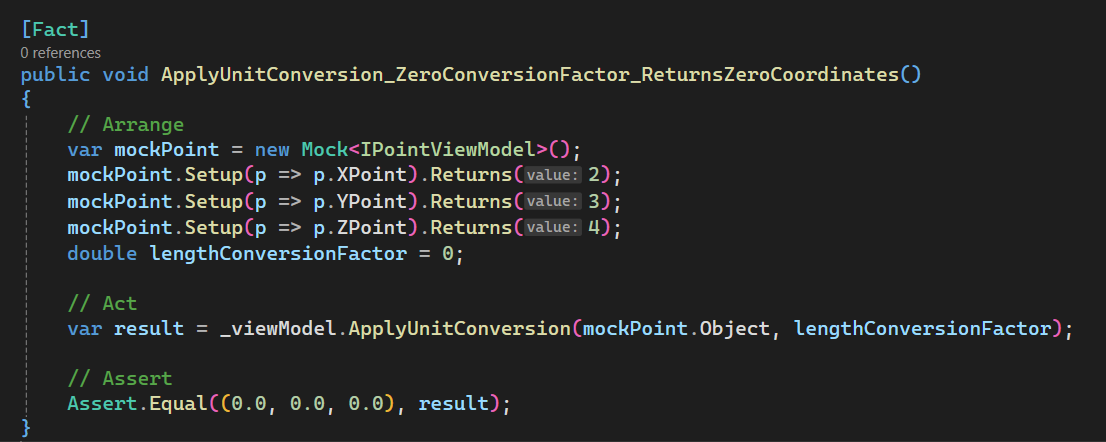
Add [Test 2]
In this section, we set up ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates.
Please see below 👇🏻 code sample for set up.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates()
{
// Arrange
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
double lengthConversionFactor = 0;
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
// Assert
Assert.Equal((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), result);
}
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
Explanation of above ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates is give below.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates()
{
}
[Fact]:- This is a test attribute.
- This attribute shows that this method is a test case that the
xUnittest runner recognizes.
public:- This means that the
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod can be accessed from anywhere. - This is important, because
xUnittest runner is external agent. xUnittest runner need to have accessed to thisApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod.- Because of this requirment we need to give
publicaccessor.
- This means that the
void:- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod. - Generally we don’t return anything from test method.
- Because of this we return
voidmeans we are not returning anything.
- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroConversionFactor_ReturnsZeroCoordinates- This is the name of method.
- This name is created in 3 different parts and combined with underscore “_“.
- Different parts are explained below 👇🏻:
- Part 1: Name of method we are testing.
- Part 2: Return value we are expecting.
- Part 3: Condition for which we are testing the method.
First we arrange our test method and setup variables and methods before testing.
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
- The explanation for the above code is in the previous section. Thus not explaining here.
double lengthConversionFactor = 0;
doubleis a data type that means “a decimal number”.lengthConversionFactoris the name of the variable.0is the value assigned to the variable.- This line creates a new variable called
lengthConversionFactorand sets its value to0.
Now we finished with our arrangement part, we will now continue with Act part of our test method.
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
varis a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable.resultis the name of the variable._viewModelis an object that represents theMainWindowViewModelview model.ApplyUnitConversionis a method of theMainWindowViewModelview model that applies a unit conversion to a point.mockPoint.Objectis the mock point object that we created earlier, which has X, Y, and Z coordinates set to 2, 3, and 4 respectively.lengthConversionFactoris the conversion factor that we defined earlier, which is 0.- This line of code is calling the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod on theMainWindowViewModelview model, passing in the mock point and the conversion factor, and storing the result in theresultvariable.
With this we finished with Act part of our test method. Now we will continue with Assert part.
// Assert
Assert.Equal((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), result);
Assertis a keyword in xUnit testing framework and is used to verify that a certain condition is true.Equalis a method of theAssertclass that checks if two values are equal.(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)is a tuple that represents the expected result. In this case, it’s a 3D point with X, Y, and Z coordinates.resultis the variable that holds the actual result of theApplyUnitConversionmethod, which we explained earlier.- Above line of code is checking if the actual result of the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod is equal to the expected result, which is the point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0).
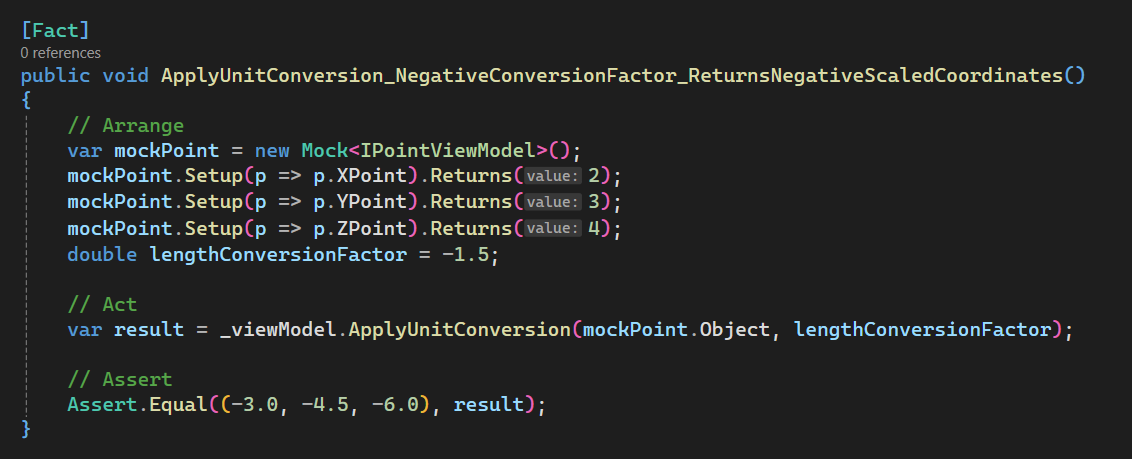
Add [Test 3]
In this section, we set up ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates.
Please see below 👇🏻 code sample for set up.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates()
{
// Arrange
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
double lengthConversionFactor = -1.5;
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
// Assert
Assert.Equal((-3.0, -4.5, -6.0), result);
}
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
Explanation of above ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates is give below.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates()
{
}
[Fact]:- This is a test attribute.
- This attribute shows that this method is a test case that the
xUnittest runner recognizes.
public:- This means that the
ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinatesmethod can be accessed from anywhere. - This is important, because
xUnittest runner is external agent. xUnittest runner need to have accessed to thisApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinatesmethod.- Because of this requirment we need to give
publicaccessor.
- This means that the
void:- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinatesmethod. - Generally we don’t return anything from test method.
- Because of this we return
voidmeans we are not returning anything.
- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_NegativeConversionFactor_ReturnsNegativeScaledCoordinates- This is the name of method.
- This name is created in 3 different parts and combined with underscore “_“.
- Different parts are explained below 👇🏻:
- Part 1: Name of method we are testing.
- Part 2: Return value we are expecting.
- Part 3: Condition for which we are testing the method.
First we arrange our test method and setup variables and methods before testing.
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(2);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(3);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(4);
- The explanation for the above code is in the previous section. Thus not explaining here.
double lengthConversionFactor = -1.5;
doubleis a data type that means “a decimal number”.lengthConversionFactoris the name of the variable.-1.5is the value assigned to the variable.- This line creates a new variable called
lengthConversionFactorand sets its value to-1.5.
Now we finished with our arrangement part, we will now continue with Act part of our test method.
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
varis a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable.resultis the name of the variable._viewModelis an object that represents theMainWindowViewModelview model.ApplyUnitConversionis a method of theMainWindowViewModelview model that applies a unit conversion to a point.mockPoint.Objectis the mock point object that we created earlier, which has X, Y, and Z coordinates set to 2, 3, and 4 respectively.lengthConversionFactoris the conversion factor that we defined earlier, which is 0.- This line of code is calling the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod on theMainWindowViewModelview model, passing in the mock point and the conversion factor, and storing the result in theresultvariable.
With this we finished with Act part of our test method. Now we will continue with Assert part.
// Assert
Assert.Equal((-3.0, -4.5, -6.0), result);
Assertis a keyword in xUnit testing framework and is used to verify that a certain condition is true.Equalis a method of theAssertclass that checks if two values are equal.(-3.0, -4.5, -6.0)is a tuple that represents the expected result. In this case, it’s a 3D point with X, Y, and Z coordinates.resultis the variable that holds the actual result of theApplyUnitConversionmethod, which we explained earlier.- Above line of code is checking if the actual result of the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod is equal to the expected result, which is the point(-3.0, -4.5, -6.0).
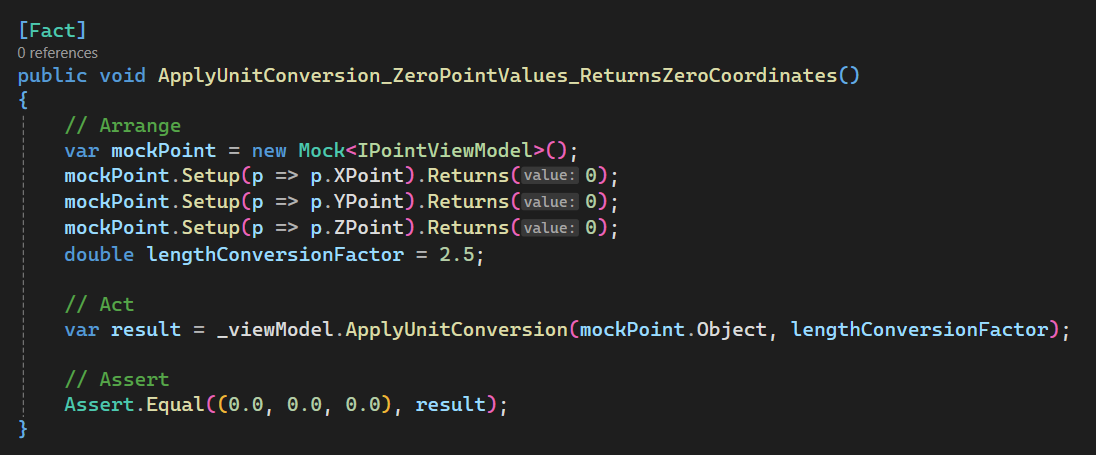
Add [Test 4]
In this section, we set up ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates.
Please see below 👇🏻 code sample for set up.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates()
{
// Arrange
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(0);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(0);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(0);
double lengthConversionFactor = 2.5;
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
// Assert
Assert.Equal((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), result);
}
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
Explanation of above ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates is give below.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates()
{
}
[Fact]:- This is a test attribute.
- This attribute shows that this method is a test case that the
xUnittest runner recognizes.
public:- This means that the
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod can be accessed from anywhere. - This is important, because
xUnittest runner is external agent. xUnittest runner need to have accessed to thisApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod.- Because of this requirment we need to give
publicaccessor.
- This means that the
void:- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinatesmethod. - Generally we don’t return anything from test method.
- Because of this we return
voidmeans we are not returning anything.
- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_ZeroPointValues_ReturnsZeroCoordinates- This is the name of method.
- This name is created in 3 different parts and combined with underscore “_“.
- Different parts are explained below 👇🏻:
- Part 1: Name of method we are testing.
- Part 2: Return value we are expecting.
- Part 3: Condition for which we are testing the method.
First we arrange our test method and setup variables and methods before testing.
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
-
var: This is a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable. -
mockPoint: This is name of object we want to create. -
new: This is a keyword that creates a new instance of a class. -
Mock<IPointViewModel>():Mockis the class that creates a “mock” object, which is a fake version of a real object.- In our case, it’s a mock version of the
IPointViewModelobject.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(0);
mockPointis the variable we created previously.Setupis a method that sets up the mock object to behave in a certain way.p => p.XPointis a lambda expression that says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty of this mock object, do something”.Returns(0)says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty, return the value0”. This means that if someone tries to get theX-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be 0.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(0);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
YPointproperty to return the value0. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Y-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be0.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(0);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
ZPointproperty to return the value0. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Z-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be0.
double lengthConversionFactor = 2.5;
doubleis a data type that means “a decimal number”.lengthConversionFactoris the name of the variable.2.5is the value assigned to the variable.- This line creates a new variable called
lengthConversionFactorand sets its value to2.5.
Now we finished with our arrangement part, we will now continue with Act part of our test method.
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
varis a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable.resultis the name of the variable._viewModelis an object that represents theMainWindowViewModelview model.ApplyUnitConversionis a method of theMainWindowViewModelview model that applies a unit conversion to a point.mockPoint.Objectis the mock point object that we created earlier, which has X, Y, and Z coordinates set to0.lengthConversionFactoris the conversion factor that we defined earlier, which is 2.5.- This line of code is calling the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod on theMainWindowViewModelview model, passing in the mock point and the conversion factor, and storing the result in theresultvariable.
With this we finished with Act part of our test method. Now we will continue with Assert part.
// Assert
Assert.Equal((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), result);
Assertis a keyword in xUnit testing framework and is used to verify that a certain condition is true.Equalis a method of theAssertclass that checks if two values are equal.(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)is a tuple that represents the expected result. In this case, it’s a 3D point with X, Y, and Z coordinates.resultis the variable that holds the actual result of theApplyUnitConversionmethod, which we explained earlier.- Above line of code is checking if the actual result of the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod is equal to the expected result, which is the point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0).
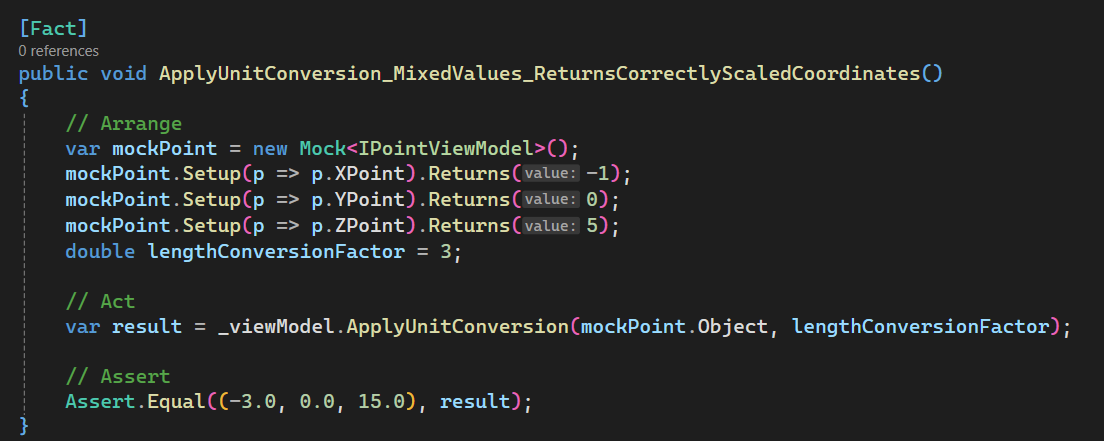
Add [Test 5]
In this section, we set up ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates.
Please see below 👇🏻 code sample for set up.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates()
{
// Arrange
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(-1);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(0);
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(5);
double lengthConversionFactor = 3;
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
// Assert
Assert.Equal((-3.0, 0.0, 15.0), result);
}
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
Explanation of above ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates is give below.
[Fact]
public void ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates()
{
}
[Fact]:- This is a test attribute.
- This attribute shows that this method is a test case that the
xUnittest runner recognizes.
public:- This means that the
ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinatesmethod can be accessed from anywhere. - This is important, because
xUnittest runner is external agent. xUnittest runner need to have accessed to thisApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinatesmethod.- Because of this requirment we need to give
publicaccessor.
- This means that the
void:- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinatesmethod. - Generally we don’t return anything from test method.
- Because of this we return
voidmeans we are not returning anything.
- This is the return type of
ApplyUnitConversion_MixedValues_ReturnsCorrectlyScaledCoordinates- This is the name of method.
- This name is created in 3 different parts and combined with underscore “_“.
- Different parts are explained below 👇🏻:
- Part 1: Name of method we are testing.
- Part 2: Return value we are expecting.
- Part 3: Condition for which we are testing the method.
First we arrange our test method and setup variables and methods before testing.
var mockPoint = new Mock<IPointViewModel>();
-
var: This is a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable. -
mockPoint: This is name of object we want to create. -
new: This is a keyword that creates a new instance of a class. -
Mock<IPointViewModel>():Mockis the class that creates a “mock” object, which is a fake version of a real object.- In our case, it’s a mock version of the
IPointViewModelobject.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.XPoint).Returns(-1);
mockPointis the variable we created previously.Setupis a method that sets up the mock object to behave in a certain way.p => p.XPointis a lambda expression that says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty of this mock object, do something”.Returns(-1)says “when someone asks for theXPointproperty, return the value-1”. This means that if someone tries to get theX-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be -1.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.YPoint).Returns(0);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
YPointproperty to return the value0. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Y-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be0.
mockPoint.Setup(p => p.ZPoint).Returns(5);
- Above line is similar to the previous one, but it sets up the
ZPointproperty to return the value5. - This means that if someone tries to get the
Z-coordinateof this fake point, it will always be5.
double lengthConversionFactor = 3;
doubleis a data type that means “a decimal number”.lengthConversionFactoris the name of the variable.3is the value assigned to the variable.- This line creates a new variable called
lengthConversionFactorand sets its value to3.
Now we finished with our arrangement part, we will now continue with Act part of our test method.
// Act
var result = _viewModel.ApplyUnitConversion(mockPoint.Object, lengthConversionFactor);
varis a keyword in C# that means “variable”. It’s used to declare a new variable.resultis the name of the variable._viewModelis an object that represents theMainWindowViewModelview model.ApplyUnitConversionis a method of theMainWindowViewModelview model that applies a unit conversion to a point.mockPoint.Objectis the mock point object that we created earlier, which has X, Y, and Z coordinates set to-1, 0, 5.lengthConversionFactoris the conversion factor that we defined earlier, which is 3.- This line of code is calling the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod on theMainWindowViewModelview model, passing in the mock point and the conversion factor, and storing the result in theresultvariable.
With this we finished with Act part of our test method. Now we will continue with Assert part.
// Assert
Assert.Equal((-3.0, 0.0, 15.0), result);
Assertis a keyword in xUnit testing framework and is used to verify that a certain condition is true.Equalis a method of theAssertclass that checks if two values are equal.(-3.0, 0.0, 15.0)is a tuple that represents the expected result. In this case, it’s a 3D point with X, Y, and Z coordinates.resultis the variable that holds the actual result of theApplyUnitConversionmethod, which we explained earlier.- Above line of code is checking if the actual result of the
ApplyUnitConversionmethod is equal to the expected result, which is the point(-3.0, 0.0, 15.0).
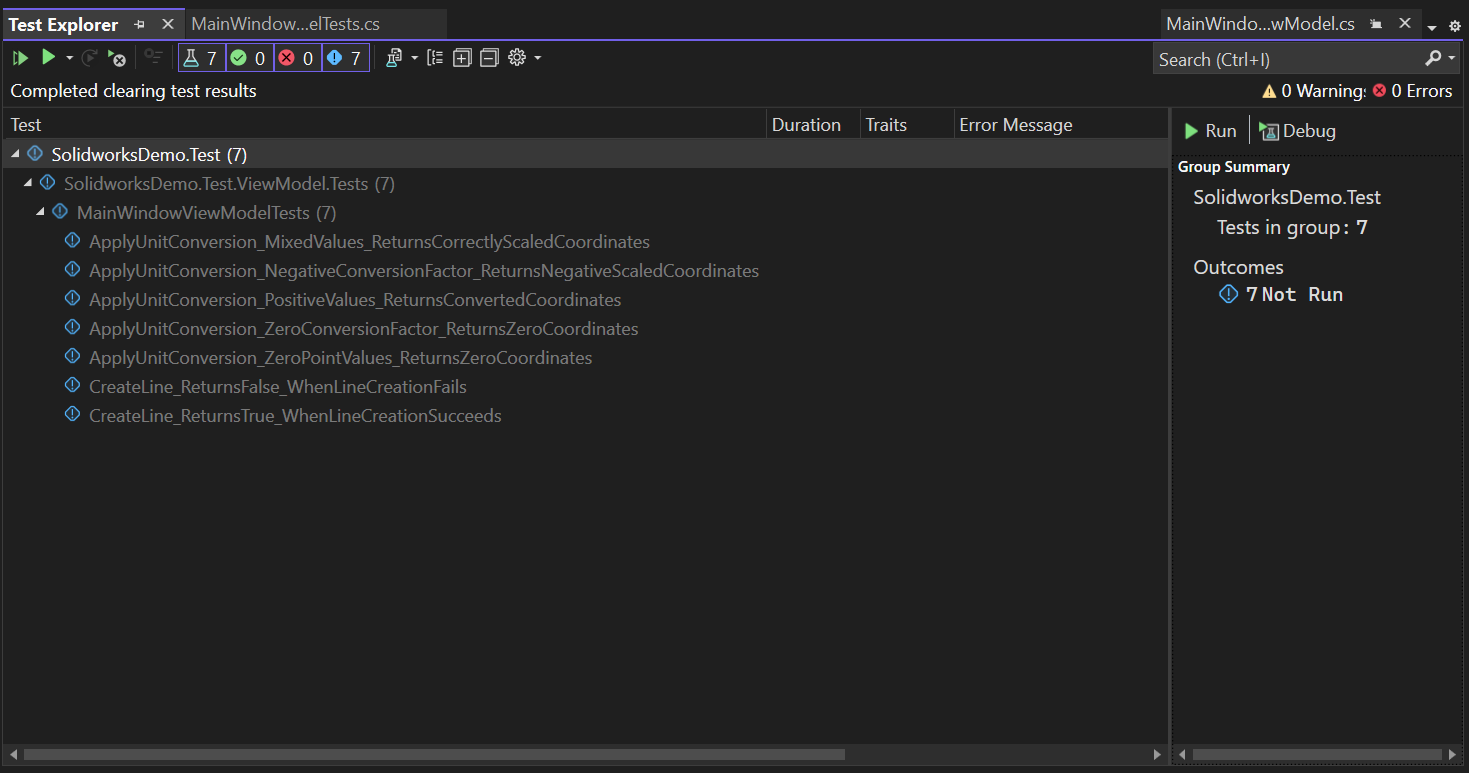
Before running test cases, we need to rebuild the Test project.
After rebuild, we see test cases in Test Explorer as shown in below 👇🏻 image.
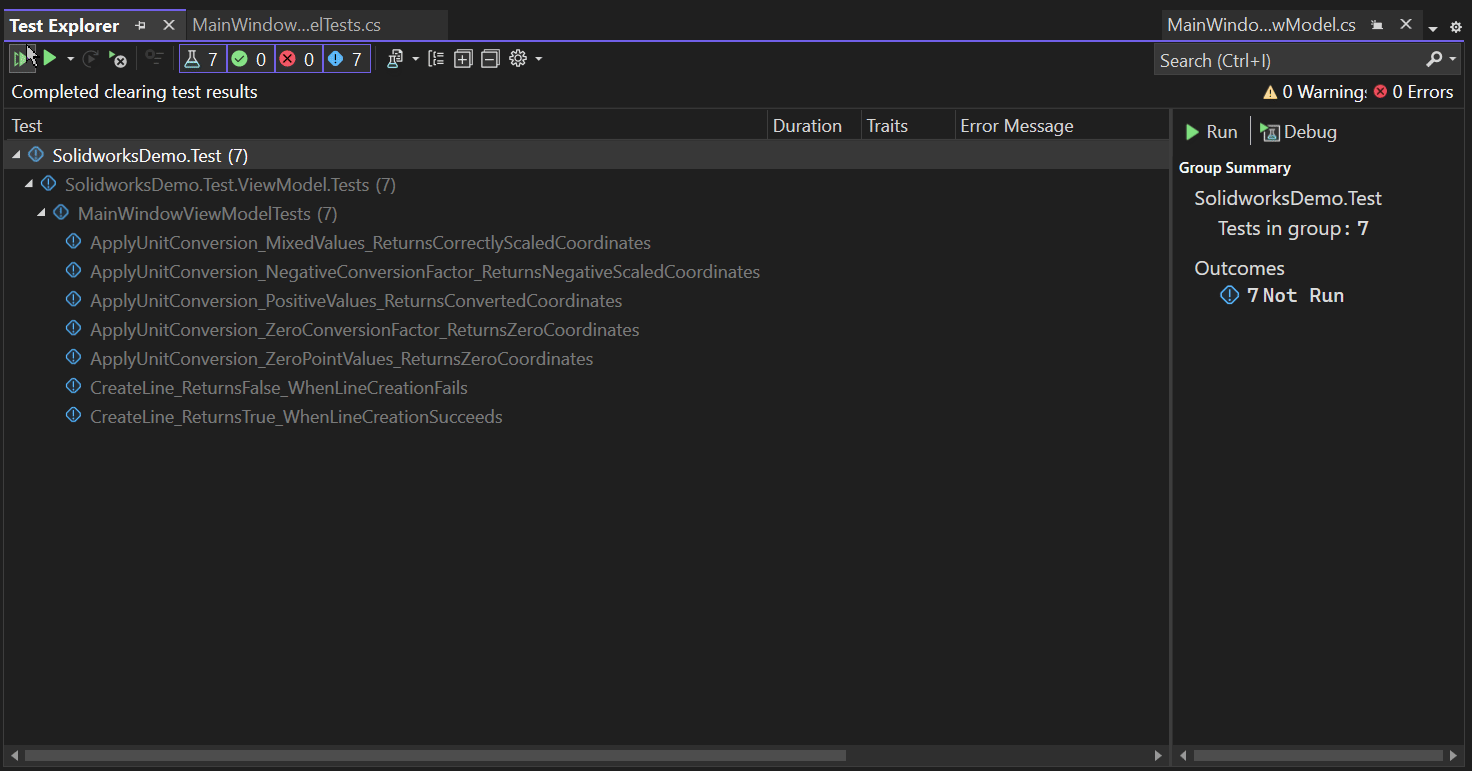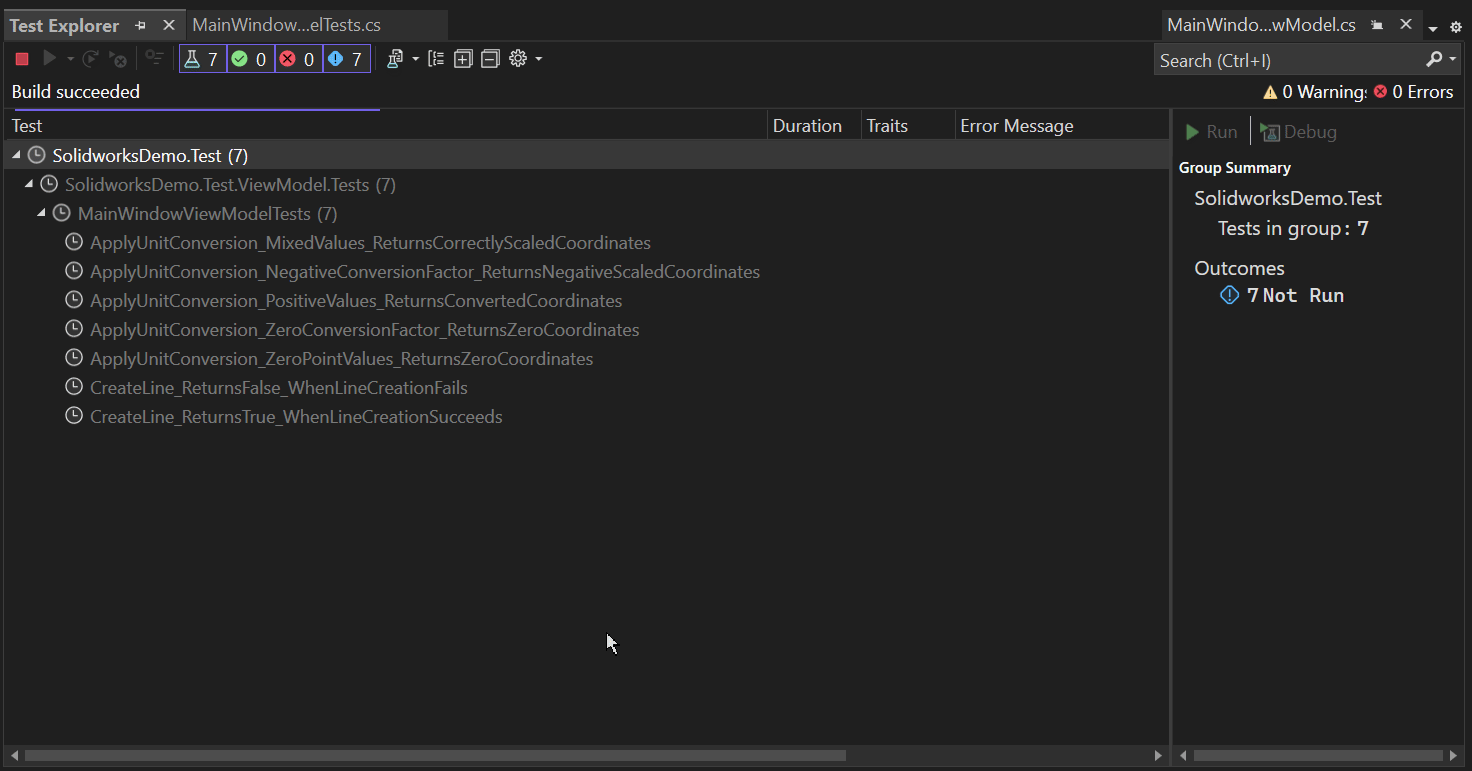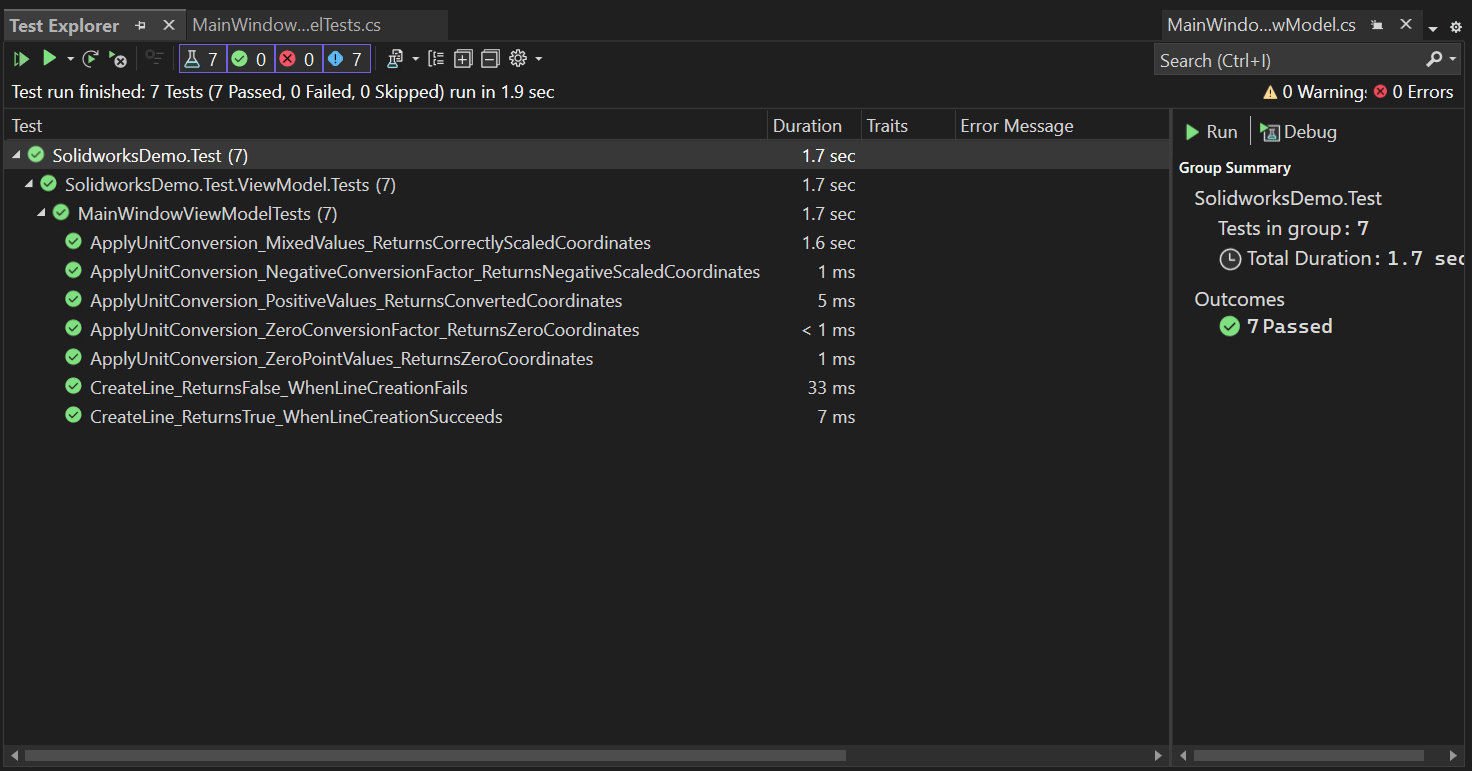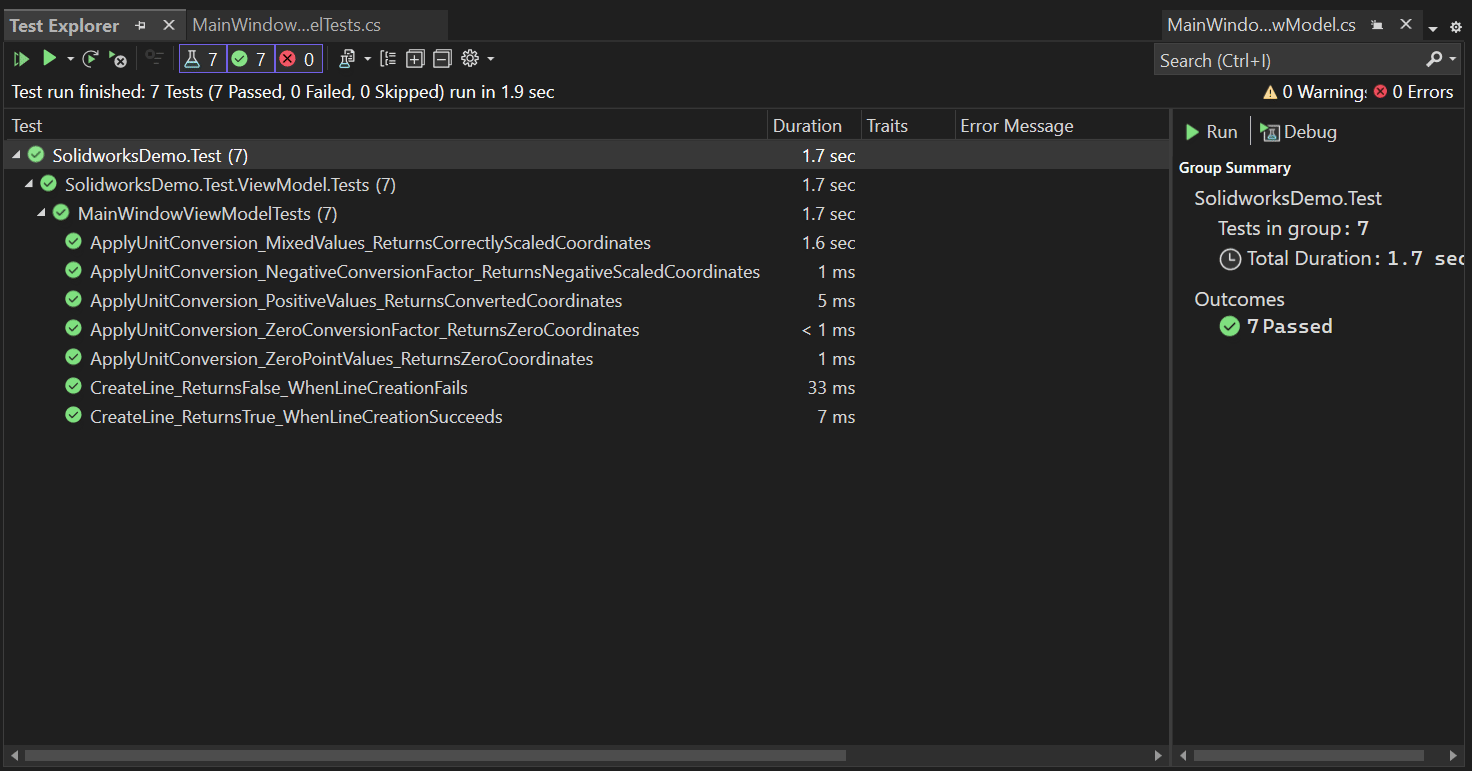
Now we run all test cases.
Please see below 👇🏻 image for reference.
This is it !!!
I hope my efforts will helpful to someone!
If you found anything to add or update, please let me know on my e-mail.
Hope this post helps you to Test ApplyUnitConversion Method.
If you like the post then please share it with your friends also.
Do let me know by you like this post or not!
Till then, Happy learning!!!